Application Notes
THERMAL CONSIDERATIONS
To use these PICO Series at full power one has to get rid of dissipated losses in the modules. Although the high efficiency of these units minimizes the heat loss; The exposed area, depending on the ambient temperature, may not be enough to keep the case temperature at an acceptable value if natural convection is used. The additional heat may be removed by a heat sink, forced air, or both. Internal losses produce heat which is moved toward the case and must be removed. Depending on the thickness and the material used, there is always a temperature gradient from inside to the case which may be calculated by:

The specification given in the data sheet of these units are such that at 85º C case the Ti; (inside temperature of components) is acceptable for proper operation. The user of these modules then has the task to keep the case temperature at or below 85º C. The temperature rise of the case depends on how efficiently the heat is removed. If the process is very efficient the thermal resistance is low and the case to ambient temperature gradient is low. The thermal resistance from the case to the air is given by:
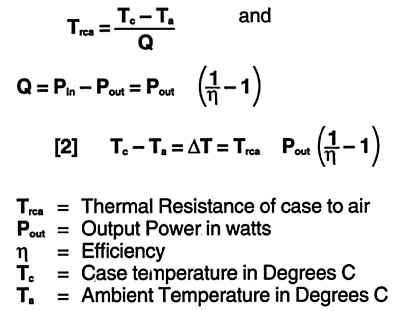
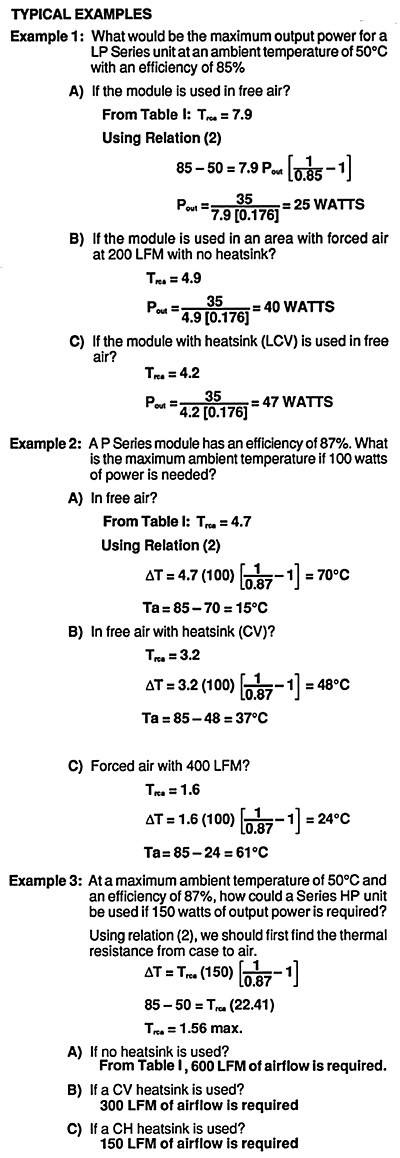
The following table shows the Thermal Resistance in free air as well as with forced cooling with or without heat sinks.
Table 1:Thermal resistance case to air (º C/W)
|
|||||||||
| . | Series LP/LF/LM | Series P | HP/XP/M Series, also Series P High Voltage Only |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseplate | Heatsink LCV |
Heatsink LCH |
Baseplate | Heatsink CV |
Heatsink CH |
Baseplate | Heatsink CV |
Heatsink |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Voltage Trimming:
The output voltage of Pico's LP, P, and HP units can be adjusted to within ± 5% of the nominal setting by placing a resistor between the "TRIM UP" and the "TRIM DOWN" pins respectively.
Due to internal tolerances, the values presented in the table are typcial. To quickly select the right resistance to achieve the desired adjustment, a multi-turn trimmer potentiometer (1M ohms) is recommended. Keep the trim resistor leads as short as possible to eliminate the stray inductance which will effect the trimming results.
|
|
|
* For LP/LF/LM Models: Trim up by adding the resistor between the Trim Pin and the -Input. Use these same resistors values.
| *Typical Resistance Range for Trim UP and Trim Down | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Resistance |
|
|
|
|
|
Resistance |
|
|
|
|
Parallel Operation
Special care must be exercised when operating these units in parallel, since these modules deliver comparatively high currents (especially the low voltage outputs of 3.3, 5.0, 5.2, and 12 volts).
For parallel operation, the corresponding pins of the units must be connected together. The paths of these connectiosn should be as direct as possible. The path to the load also should have the lowest possible resistance; otherwise unacceptable losses and load regulation will occur. For instance, a 1 milli-ohm resistance and a 100 ampere load will cause 10 watts of line losses as well as additional load regulation.
If the parallel configuration is for redundant operations, schottky diodes should be used at the output of each module as shown.
For parallel operation, add suffix P to Part #. Example: PA5SP, PB5SP, PC5SP, PD5SP.

Use of a Shutdown Pin
With the help of a shutdown pin, one may turn the unit on and off. If the voltage across the shutdown pin with respect to the -input pin is reduced to 0.15 volts or lower, the converter shuts off. When more than one module has to be shut down at the same time, one must use a circuit similar to the one below.

Noise Reduction
For additional noise reduction, a circuit as shown below is suggested. If further reduction is required, filters at the input and output may be required. Please call the factory.

Overload Protection
There is an overload protection of 10% to 20% above the maximum load current installed in each unit. If there is a large capacitive load, or if the unit initially requires a much larger starting current than the peak power available, please call the factory for further consultation. Special units with different overload protection may be required.
For immediate engineering assistance or to place an order:
Call Toll Free: 800-431-1064
PICO Electronics, Inc.
143 Sparks Ave. Pelham, NY 10803-1837
Tel: 914-738-1400 or Fax: 914-738-8225



